Astronauts leave behind many things when they take on a space journey. Bacteria, however, stay with them.
Extreme spaceflight conditions can force these bacteria to toughen up, while simultaneously lowering the immune defences of the stressed, isolated crew. These effects —and the risk of infection— grow with mission duration.
Now researchers have taken another small step towards deep space exploration, by testing a new silver- and ruthenium-based antimicrobial coating aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Published in Frontiers in Microbiology, their study shows that the AGXX dramatically reduced the number of bacteria on contamination-prone surfaces – and could help protect future astronauts beyond the moon and Mars.
A perfect storm
Microgravity. Cosmic radiation. Psychological stress. Unearthly conditions at the ISS create a perfect storm of weakened immune system and strengthened bacteria, that can put its crew at risk.
"Spaceflight can turn harmless bacteria into potential pathogens," said senior study author, Prof. Elisabeth Grohmann, of Beuth University of Applied Sciences Berlin. "Just as stress hormones leave astronauts vulnerable to infection, the bacteria they carry become hardier – developing thick protective coatings and resistance to antibiotics – and more vigorous, multiplying and metabolising faster."
To make matters worse, the genes responsible for these new traits can be readily shared among different species of bacteria, via direct contact or in the ‘matrix’ of slime they secrete – creating new bad guys, Agent Smith-style.
The silver lining
To address this problem, Grohmann and colleagues tested a new antimicrobial coating, AGXX, on a contamination-prone surface aboard the ISS: the toilet door.
"AGXX contains both silver and ruthenium, conditioned by a vitamin derivative, and it kills all kinds of bacteria as well as certain fungi, yeasts and viruses. The effects are similar to bleach – except the coating is self-regenerating so it never gets used up," explained Grohmann.
Silver on its own has been used since prehistory to prevent microbial growth. Today it is found in everything from socks to swimming pools – which is perhaps why resistant bacteria have begun to emerge. AGXX is one of the latest attempts to reinvigorate this ancient antimicrobial.
A ray of hope
According to the product website, AGXX is a specifically structured and coated silver surface that has been refined and conditioned by further treatment. Its antimicrobial action mainly takes place on or very close to the AGXX surface by depolarising biological membranes and subsequent cell lysis.
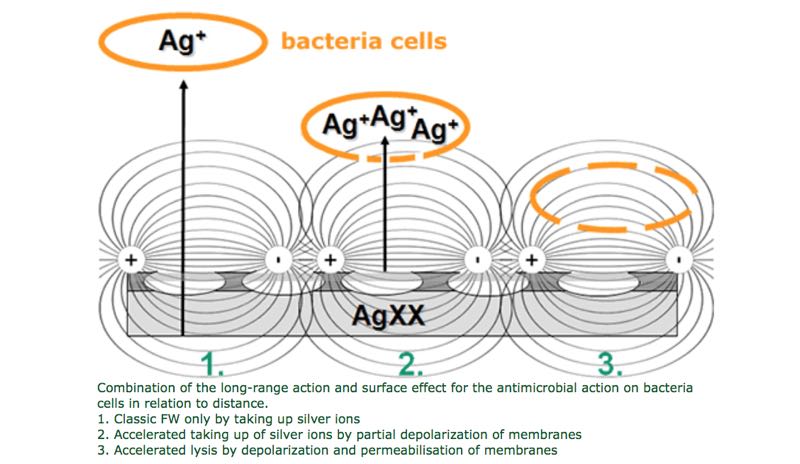
Photo as seen on AGXX product website
The AGXX coating proved to be highly effective.
“After 6 months exposure on the ISS, no bacteria were recovered from AGXX-coated surfaces,” Grohmann reported.
Even at 12 and 19 months, a total of just 12 bacteria was recovered – a reduction of 80% compared to bare steel. A regular silver coating tested for comparison had only a slight antimicrobial effect, reducing the number of bacteria by 30% versus steel.
“With prolonged exposure time a few bacteria escaped the antimicrobial action. The antimicrobial test-materials are static surfaces, where dead cells, dust particles and cell debris can accumulate over time and interfere with the direct contact between the antimicrobial surface and the bacteria.”
Weathering deep space
“Most importantly, no serious human pathogens were found on any surface. Thus, the infection risk for the ISS crew currently is low,” stressed Grohmann.
Nevertheless, all bacterial isolates were able to form immunity-evading slimy coatings, and most were resistant to at least three antibiotics. They were also able to share the genes responsible.
“Immunosuppression, bacterial virulence and therefore infection risk increase with duration of spaceflight. We must continue to develop new approaches to combat bacterial infections if we are to attempt longer missions to Mars and beyond,” Grohmann concluded.
The researchers said they will continue to analyse the antimicrobial performance of AGXX, most recently aboard the joint IBMP-NASA SIRIUS 18/9 isolation mission./p>
The study, entitled "Biofilm Forming Antibiotic Resistant Gram-Positive Pathogens Isolated From Surfaces on the International Space Station", is available online.
