In conversations leading up to establishing an online particle monitoring systems, most cleanroom users mention the following request for their User Requirement Specification (URS) document: “IQ, OQ and PQ will be provided by the supplier”.
The IQ, OQ and PQ acronyms stand for installation, operation and performance qualification, respectively. Unfortunately, there are many wrong or misleading points in that statement. The major one is asking for Performance Qualification from the same vendor who is also offering the Installation and Operational Qualification.
PQ verifies if the overall system meets the URS and should be performed with all attributes taken into account, such as HVAC system, machines, production attributes, final product quality and its effects on patient health.
Online monitoring system vendors can provide proper IQ and OQ, but as the party fully responsible for the end performance, the end-user must carry out PQ, checking that the system meets their initial requirements as recorded on the URS.
All these qualification activities on the right side of GAMP 5 V Scheme (Verification Steps) are also referring to specification steps.
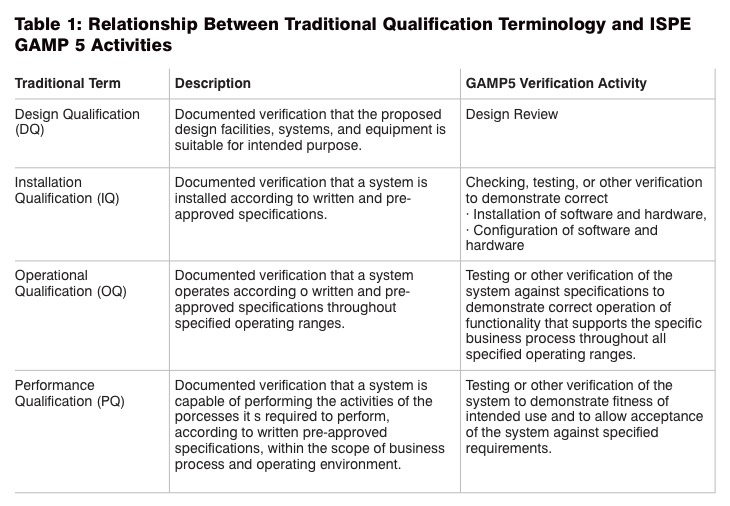
This article covers IQ and OQ with parameters that are included in these qualification steps. Table 1 defines and describes all the verifications activities that are prescribed in ISPE GAMP5.
Installation Qualification
The initial objective of Installation Qualification is to verify Configuration Specifications. This document details the tests that are required to verify that all environmental monitoring system equipment and software detailed within the Design & Configuration Specifications have been installed and are functional.
These tests are to be conducted once the system has been installed and commissioned. The IQ document contains the test rationale, protocols and results needed for these tests.
What should be included in an IQ document?
- Mention the name of document producers, signees with their authority in the Document Review and Approval section
- Write a brief Introduction section to explain document details
- Write an Overview to describe the system, intended use, location (address) and test outline
- Mention all Reference Documents in a separate section. Documents like User Requirement Specification, Functional
Specification and Design Specification should be listed with document and revision numbers
- Write proper Test Plan to describe entire test steps, acceptance and rejection criteria, test incident procedures if any.
- Both tester and witness should be able to easily understand this lean description to execute this without additional knowledge
- List Test Equipment that the tester and witness will use during IQ
- List all Test Personnel (both end-user and vendor with company name, printed name, signature and initials)
- IQ Tests and explanations
- Test Incident Records and Reports
- Final Review Report
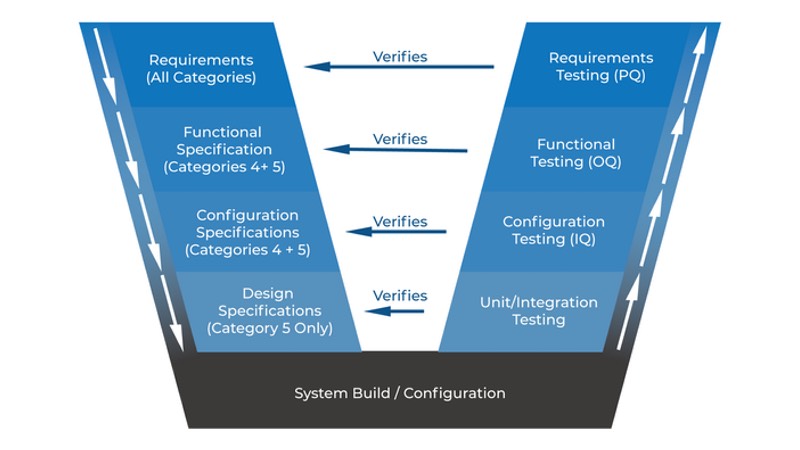
Read the previous article of the series to find out more about the GAMP5 V scheme
IQ tests
During IQ, the following tests should be done and verified for online monitoring systems (tests are not limited to these steps, tests can be added based on Design & Configuration Specifications).
- Documentation/Drawings
This test checks that cabinet wiring diagrams, system diagram, hardware technical manuals and system connection/layout diagrams are in place. This step also verifies that Design and Configuration Specifications for the system are in place. - Monitoring Computer System and Software
Testing should also be done to ensure that the computer system is suitable, using the correct operating system as specified in Functional Specification. PC model, make, operating system, software model and version should be checked and verified. - System Control Cabinet
This test is to check that the cabinet has been built to an acceptable standard, secure termination of wires, labelling of all modules, power supply and cables should be verified and all related manuals and technical documents should be in place. - Sensors and Alarm Devices
Online particle counters, online microbiological air samplers, environmental sensors, alarm towers, buzzers, etc will be listed separately. Each sensor and interface will be verified, to ensure that the correct model has been supplied and that each is installed correctly. Equipment serial number & model/make verification, technical installation verification, secure mounting check, labelling control should be performed and recorded.
Operational Qualification
Upon completion of Installation Qualification, Operational Qualification tests verify that a system operates accordingly to written and pre-approved specifications throughout specified operating ranges.
Operational Qualification verifies specs that are clearly mentioned and covered in the Functional Specification.
What should be included in the OQ document?
- Mention the name of document producers, signees with their authority at Document Review and Approval section,
- Write a brief Introduction section to explain document details,
- Write an Overview to describe the system, intended use, location (address) and test outline,
- Mention all Reference Documents in a separate section. Documents like User Requirement Specification, Functional
Specification, Design Specification and Installation Qualification should be listed with document and revision numbers.
- Write proper Test Plan to describe entire test steps, acceptance and rejection criteria, test incident procedures if any.
- Both tester and witness can easily understand this lean description to execute this file without additional knowledge.
- List all Test Equipment that testers and witnesses will use during Operational Qualification
- List all Test Personnel (both end-user and vendor with company name, printed name, signature and initials)
- OQ tests and explanations.
- Test Incident Records and Reports
- Final Review Report
OQ tests
During OQ, the following tests should be done and verified for online monitoring systems (tests are not limited to these steps, tests can be added based on Functional Specification. The main idea here is to verify all operational attributes and qualify them to prove their functional specifications).
- System Power up/Power Down Tests
This test step verifies that the system powers up/down and continues collecting data. During this test, the tester should also verify system clock vs software clock by comparing event logbook time records to the operating system clock. - Security
To verify different user levels and their privileges/limitation, several scenarios should be written in the security test steps. User, Power User and Administrator privileges should be clearly defined, tested and verified with several tests to ensure that user levels are up and running as planned in Functional Specification to meet the URS. To perform this test steps, different user accounts should be created and password for these test accounts should also be recorded. - Report Interface (Tables, Maps and Plots) Tests
The requirement of the system’s ability to report data over a specific time frame is important. The aim here is to check and verify that the raw data for a specific time frame matches the report, table and/or graph that the system generates. Different test scenarios should be created to verify this 100% match. - Sensors and Alarm Interface Tests
Each and every sensor (remote particle counters, microbiological active air samplers, temperature and relative humidity sensors, differential pressure sensors, etc) and alarm interfaces (alarm towers, buzzers, etc) should be tested and verified. Operational testing for particle counters will be zero count tests, accurate particle sampling test with simulation of particles at each location, start and stop time checks via audit logs etc. The aim here is to verify that the sensors are meeting (or even exceeding) requirements that are mentioned in Functional Specification. - Alarm Scenario Tests
Alarm scenario testing verifies that the software indicates alarms in real time, logs the alarms and triggers once the limits are exceeded. To test different alarm scenarios, limits could vary from the actual system alarm limits. The aim here is to demonstrate alarm conditions match the plan. Software alarm colour coding, messages, colour alarm towers, buzzers and other indicators that generates alarm output should all be tested for different scenarios and verified. - Event Log
The objective in this event log test step is to verify the system Audit trail is capturing all events in the System Event log. All user logins, logouts, data downloaded, archives and changes to software graphs, data tables, reports and properties are logged in the event log. Users can view the event log to track what has occurred in the system. - Back up and Recovery
As structured during Functional Requirement Specification, system backup, and recovery testing should be performed as per written in the protocol. Defining responsible parties, software features, directories and the assigned location for back-up files should also be the part of this test step.
The last article of the series will be published in the December issue. It will cover environmental monitoring system maintenance and data interpretation.
N.B. This article is featured in the November 2019 issue of Cleanroom Technology. Subscribe today and get your print copy!
The latest digital edition is available online.

