Verifying ambient conditions that may affect product quality within a cleanroom is called Qualification Activity (QA). It is good practice that qualification activities are well planned, taking the life cycle of the facility, equipment, utilities, process and product into consideration while providing appropriate quality oversight across the entire qualification cycle.
The key elements of the site qualification programme should be clearly defined and documented in a Validation Master Plan (VMP) or equivalent document.
During qualification activities, a large amount of documentation is produced, which if not assigned properly, could result in the qualification process being compromised.
A robust risk management approach is, therefore, mission-critical, and should be utilised for qualification activities, in light of increased knowledge and understanding from any changes during the project phase.
Documentation is king
The way in which risk assessment (RA) is used to support qualification activities should be clearly documented. RA should be carried out where there may be in direct contact with the product to mitigate any risks of failure.
A formal release for the next stage in the qualification and validation process should always be authorised by the relevant responsible personnel, who would also grant conditional approval to proceed to the next qualification stage.
According to the EU GMP Annex 15, reviews and conclusions of the validation should be reported and results summarised against acceptance criteria. Any subsequent changes to acceptance criteria should be scientifically justified and a final recommendation made as to the outcome of the validation.
Companies need a process or system that reduces the time spent on performing the area qualification and paperwork, minimising human error, streamlining recordkeeping and review aspects of the qualification
Improved productivity and reduction of costs while also meeting regulatory requirements are at the forefront of QA and Validation departments of any company that requires cleanrooms. Cleanrooms also require periodic qualification, hence companies need a process or system that reduces the time spent on performing the area qualification and paperwork, minimising human error, streamlining recordkeeping and review aspects of the qualification.
Paperless method
A paperless protocol that can reconfigure tests and calculations to suit the instrument being tested provides a clear advantage over a static manual paper-based process.
Plus, paperless protocols reduce the person-hours spent developing and cataloguing protocols for each area of a cleanroom while meeting all of the required industry standards.
Certilabo, for example, is a strategic tool that focuses on the concept of cleanroom qualification in accordance with international standards and guidelines. This unique software enables validation professionals and engineers in the pharmaceutical, healthcare, electronics and food industry to perform, approve and complete cleanroom validation protocols at different locations and facilities.
Using paperless software is a comprehensive solution that provides fast, efficient and reliable storage of complex cleanroom validation data while meeting requirements defined within EU GMP Annex 11, 21CFR part 11, ISPE GAMP.
IQ to PQ protocols
Paperless IQ to PQ protocols include entries for all necessary data, which in essence provide a checklist ensuring that all required information is recorded, including company information, instrument information, required calibrated qualification tools, standards, detailed test procedures, explanation of equations used for all tests and final results.
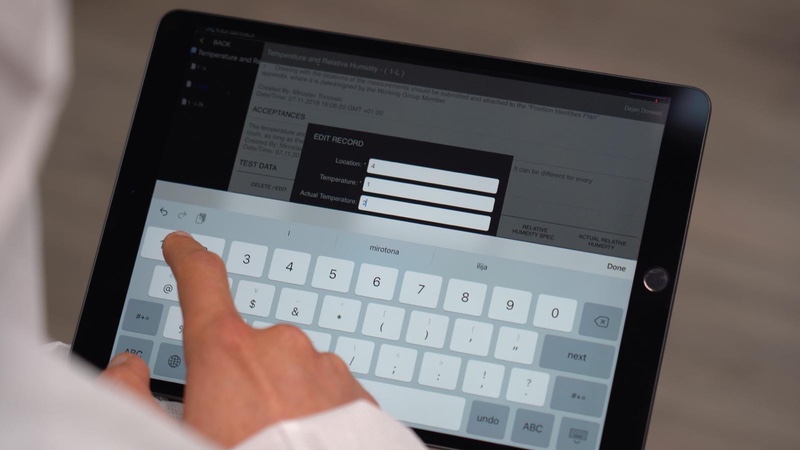
Once the information about the company and facility is entered on the facility page of the application, the data re-populates throughout the document and is automatically displayed at the bottom of each page.
Implementation considerations
To implement the usage of paperless software solutions, companies should first understand their current state and acceptability of control based on risk to data integrity. This activity must be particularly applicable to commercially available products.
Focusing on the organisational/procedural controls is an appropriate place to start, and a well-defined strategy is key to the success of starting the use of paperless qualification solutions.
There is no single approach when it comes to implementing a paperless software solution; however, there are some elements that can increase the likelihood of success, for example, does it help to realise a positive return on investment?
The strategy for the paperless qualification software should define the reporting expectations to senior management, QA, Validation Team Leaders, Project Engineers as well as operational users. It can be an opportunity to share qualification results and progress to date against the plan. It can also identify and communicate issues and provides a mechanism to agree on next steps.
This a high-level plan for executing the cleanroom qualifications by paperless software solutions should define the approach, timeline, and resource requirements, in other words, paperless qualification protocols should:
- Serve as a mechanism to track complete qualification progress
- Demonstrate a commitment to identifying and addressing deviations during the qualification processes.
- Provide a documented rationale and plan to outline the program and actions during audits and inspections
Audit processes can be key to the success of paperless qualification solutions. Several types of audits should be performed, for example:
- Initial gap assessment or audit of nonconformance
- Periodic audit of long term data archives
- Closeout gap assessment or full audit following program completion
- Ongoing internal quality audits to ensure continuing effectiveness and compliance of the qualification process
Audits will provide critical information for these software solutions; will set a baseline and measure the success of implementation as well as highlight possible gaps and possible corrections and additions to qualification scope.
Business continuity
For the availability of commercial software solutions that support critical processes, such as cleanroom qualification, provisions should be made to ensure continuity of support for those processes in the event of a system breakdown, for example through manual or alternative systems.
The time required to bring the alternative arrangements into use should be based on risk and appropriate for a particular system and the business process it supports. These arrangements should be adequately documented and tested.
Reference:
- GMP Annex 11 – Computerised Systems
- GMP Annex 15- Qualification and Validation
- GAMP 5 – Records and data integrity
- GAMP 5 – A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems
- ISO14644 -3:2019 – Test Methods
- ISO14644-1:2015 - Classification of air cleanliness by particle concentration
N.B. This article is featured in the December 2019 issue of Cleanroom Technology. Subscribe today and get your print copy!
The latest digital edition is available online.




